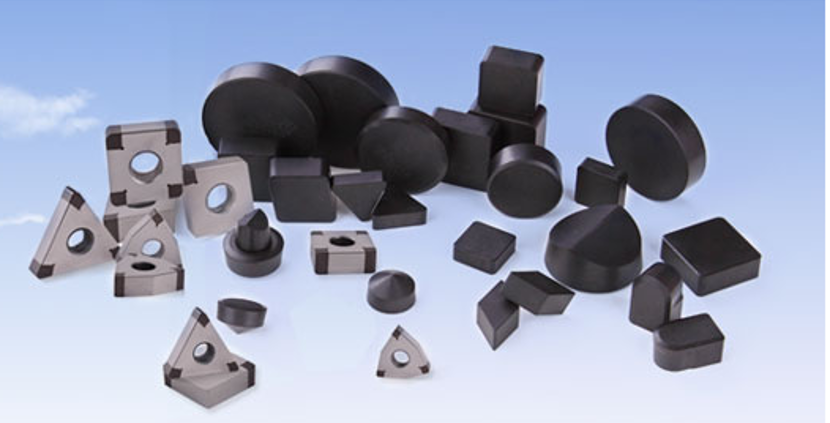
Polycrystalline cubic boron nitride (PCBN) is based on cemented carbide, and a layer of cubic boron nitride (CBN) single crystal fine powder (0.5~1.6mm thick) is placed on it, and the binder is subjected to high temperature (1400~2600 ℃) and high pressure (7~9Gpa) to press the polycrystalline tool material.
Due to the small particle size of single crystal CBN powder and the existence of “cleavage planes” that are easy to split, single crystal CBN powder cannot be directly used to manufacture cutting tools. Therefore, most of the cutting tools used in the industry are polycrystalline cubic boron nitride (PCBN).
PCBN Blank and Cutters
1.Properties of PCBN
1.1 High Hardness and Excellent Wear Resistance of Cubic Boron Nitride CBN)
CBN is artificially synthesized, its hardness is second only to that of diamond, and the grain hardness can reach HV8000~ HV9000, which is much higher than that of ceramics and cemented carbide. The hardness of the PCBN composite sheet (usually HV3000 ~ HV5000) mainly depends on the content of CBN. Generally, the content of CBN is between 40% and 95%. The hardness of PCBN increases with the increase of CBN content. The relationship between wear resistance and CBN content is not a monotonic relationship, and there are different optimal values under different processing conditions. When machining heavy steel molds, when the CBN content is about 55%, the tool is the most wear-resistant.
CBN is artificially synthesized, and its hardness is second only to that of synthetic diamond powder. The grain hardness can reach HV8000~HV9000, which is much higher than that of ceramics and cemented carbide. The hardness of the PCBN composite sheet (usually HV3000 ~ HV5000) mainly depends on the content of CBN. Generally, the content of CBN is between 40% and 95%. The hardness of PCBN increases with the increase of CBN content. The relationship between wear resistance and CBN content is not a monotonic relationship, and there are different optimal values under different processing conditions. When the CBN content of PCBN is about 55%, its tool processing mold heavy steel is the most wear-resistant.
1.2 High Thermal Stability of Cubic boron nitride (CBN)
The heat-resistant temperature of cubic boron nitride is as high as 1400 ~ 1500 ℃, which is almost double that of diamond (700-800 ℃). Cubic boron nitride is transformed from cubic crystal to hexagonal crystal and begins to soften when it is above 1370 °C. It can be used to make tools for high-speed cutting of superalloys, and its cutting speed is 3-5 times higher than that of cemented carbide tools.
1.3 Excellent Chemical Stability of Cubic Boron Nitride(CBN)
Cubic boron nitride is a very chemically inert substance. In neutral reducing gas medium, it is stable to acid and alkali. It only reacts with carbon at above of 2000 °C and does not react with iron group materials at 1200~1300 °C. The bonding and diffusion effects of cubic boron nitride (CBN) and various materials are much smaller than those of cemented carbide, and can be used to cut steel materials that industrial diamond powder cannot cut.
1.4 Excellent Thermal Conductivity of Cubic Boron Nitride
The thermal conductivity of cubic boron nitride is 79.54w/m.k, which is second only to diamond (146.5w/m.k). And with the increase of temperature, the thermal conductivity of cubic boron nitride gradually increases, which is beneficial to the temperature control of the cutting area and the reduction of the diffusion wear of the tool.
1.5 Low Coefficient of Friction of CBN
The friction coefficient between PCBN and different materials is 0.1~0.3. The lower friction coefficient reduces the cutting force, reduces the cutting temperature, and is not easy to generate chips, which is beneficial to improve the surface quality of the processed material.
2. Classification of Polycrystalline Cubic Boron Nitride(PCBN)Tool
Polycrystalline cubic boron nitride (PCBN) cutting tools can be divided into Monolithic Polycrystalline Cubic Coron Nitride sintered body (referred to as PCBN sintered body) and polycrystalline cubic boron nitride composite sheet (referred to as PCBN composite blade) and Electroplated cubic boron nitride cutting tools are most widely used with PCBN composite inserts.

PCBN Tools
3. Application of PCBN Cutters
PCBN is composed of numerous small disordered CBN single crystals, no cleavage plane, macroscopic directionality, which will greatly reduce the effect of splitting, and new crystals are continuously exposed as the cutting tool wears away. PCBN has similar structure and properties with PCD and PDC tool materials, but its wear resistance is worse than that of PCD and PDC. PCBN has good chemical corrosion resistance and shows good thermal stability at the high temperature of 1200℃. Therefore, the high temperature does not have any adverse effect on the PCBN tool tip, on the contrary, it can also play a role in accelerating the cutting of hard iron alloy.
With the continuous development of cutting technology, cubic boron nitride tool is widely used in the machining of high hardness and difficult materials.
3.1 Turning Hard-to-machine Materials with High Hardness by CBN tools
Due to the high hardness and wear resistance of CBN tools, the use of integral PCBN cutting tools can be used for grinding and turning high-hardness and difficult-to-machine materials.
3.2 High Speed and Ultra-high Speed Cutting by PCBN Tools
PCBN tools are most suitable for high-speed cutting of cast iron and hardened steel materials. When the PCBN tool cuts cast iron and hardened steel, it can be seen from the relationship between the tool flank wear and the cutting distance that when the cutting speed exceeds a certain limit, the higher the cutting speed, the smaller the PCBN tool flank wear speed. It means that the life of the tool under high-speed cutting is higher, which is especially suitable for modern high-speed cutting.

Processing Hardened Steel by PCBN
3.3 Dry Cutting by PCBN Tools
CBN tools use dry cutting when machining workpieces, which can reduce environmental pollution. The use of coated or ceramic tools requires wet cutting, and iron filings are not easy to clean. The use of CBN tool can not only cut high-hardness cast iron with a large margin without adding cutting fluid, but also ensure on-site hygiene and facilitate the recycling of iron filings.
3.4 Automatic and Difficult to Process Material Processing by PCBN Tools
PCBN tools have high hardness and wear resistance, which can process high-precision parts for a long time at high cutting speeds, greatly reducing the number of tool changes and the time spent on tool wear compensation downtime. Therefore, PCBN tools are very suitable for CNC machine tools and processing equipment with a high degree of automation, which can fully utilize the high efficiency of the equipment.

Application of PCBN in automatic machining
4. Service Life of PCBN Tool
The life of PCBN tools is 3-5 times that of ceramic tools and 5-15 times that of carbide tools. Its high wear resistance and long life greatly improve the machining accuracy of the workpiece, reduce the number of tool changes and sharpening, and improve work efficiency.
In recent years, with the rapid development of CNC (computer numerical control) processing technology and the widespread use of CNC machine tools, the application of PCBN tools that can achieve high efficiency, high stability and long life processing has become increasingly popular. Machining concepts, such as high-speed cutting, hard machining, turning grinding, dry cutting, etc. PCBN tool material has become an indispensable and important tool material in modern machining.


