I.Cultivation method of Lab-Grown Diamond
Lab-grown diamond refers to the appearance, chemical composition and crystal structure of natural diamond crystal made in a laboratory or factory through certain technology and process. It is a polycrystalline diamond polymerized from diamond crystals 10 to 30 nanometers in diameter. Synthetic diamond has a history of sixty or seventy years. With the continuous development of science and technology, there are not only diamond materials for industrial applications but also synthetic diamonds with gem characteristics.
There are two production processes for lab-grown diamonds: high pressure and high temperature method(HPHT)and chemical vapor deposition(CVD)method.
(1)High Pressure and High Temperature Method (HPHT)
As early as 1954, scientists came up with the idea to create the first diamond in a laboratory by simulating the environment in which natural diamonds grow in nature and by putting extremely high pressure and high temperature (HPHT)in a large machine. There are mainly three kinds of equipment to simulate the environment of natural diamond formation: Cubic Press (Cubic Press), two-section ball Press and Belt Press.
HPHT method is the original diamond cultivation method and is often used to change the color of diamonds, such as pink, blue and green. At present, pure carbon is melted at temperatures of 1300-1600 °C and pressures of 870,000 LBF/In2 and deposited on diamond crystals for cooling and precipitation. Due to the machine structure, size and growth process limitations, it is difficult to cultivate large diamonds by the HPHT method, so it is mostly used to produce a small lab-grown diamond. Most diamond colors can reach D~F colorless, except for a small part of the laboratory diamond has not overcome the technology will be below H color; Most of the clarity is VS~SI grade, the slower the growth rate, the higher the clarity, and vice versa.
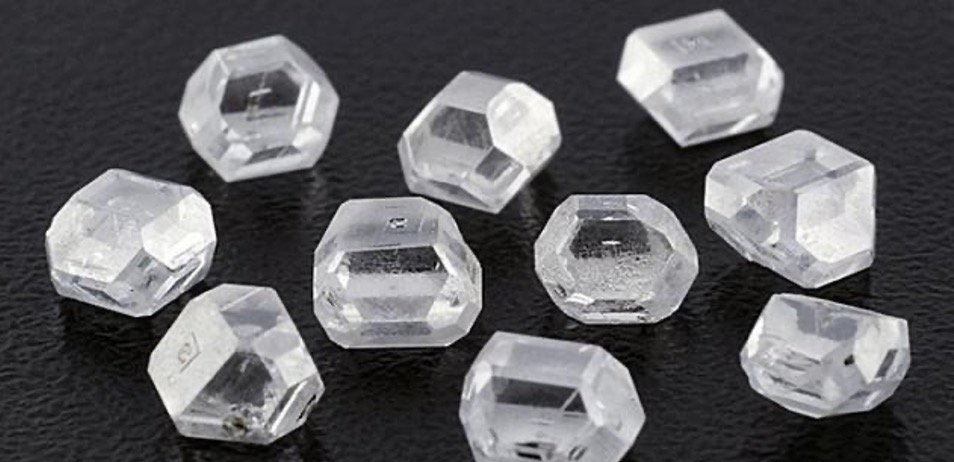

(2) Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
In 1960, in order to improve the disadvantages of HPHT production method, scientists invented Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This method uses a diamond plate as the seed, puts it into a vacuum environment, removes all impurities, and warms the environment to 800-1200 ℃. Inject hot methane and hydrogen, and use microwaves to release the carbon atoms in the methane. This carbon will slowly deposit on the diamond seeds, replicating the structure of the seeds and slowly growing. The color of CVD cultured diamond is mainly F~H, and the cleaner the impurities are removed in vacuum, the better the color. In terms of clarity, most of CVD diamonds exceed HPHT diamonds, generally between VVS~VS.
The diamond that laboratory cultivates comes to call rough diamond, a rough diamond looks humble, must pass careful cutting and grind process, just can become the diamond that we see flashing and brightness.
III. Screening of Lab-grown Diamond
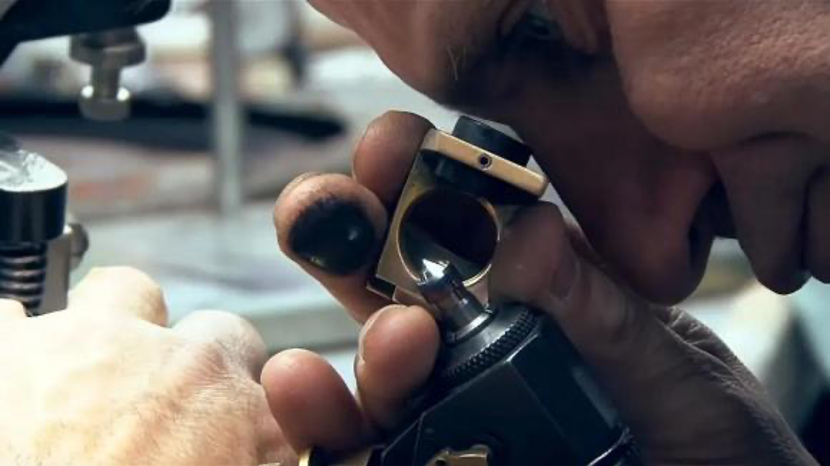
Sorting lab-grown rough diamonds into various categories requires skilled and trained sorters. They evaluate each diamond for its characteristics and sort them into different types, color, clarity, carats and shape.
VI. The marking for Diamond
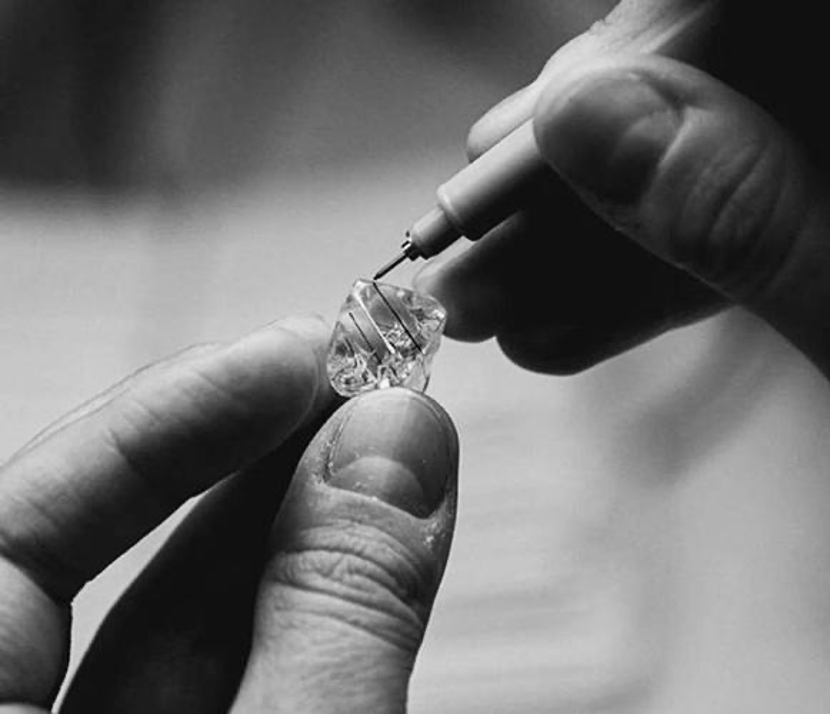
Diamond lineation is marking the surface of a diamond. This is the first step in diamond cutting, which involves examining rough diamond and marking the surface of the diamond by experienced and skilled workers. The ultimate goal is to produce the largest, cleanest, most perfect diamond to represent the value of a diamond as high as possible.
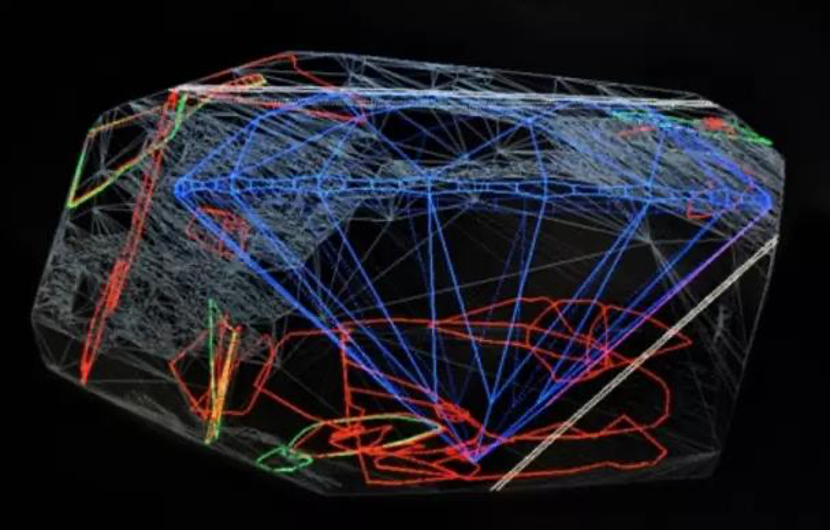
Scribers need to maintain the original weight as much as possible while minimizing inclusions. The scriber uses a magnifying glass to study the structure of the diamond blank, which can take months for large diamonds and minutes for an ordinary rough diamond. No matter how small the diamond, each diamond needs to be examined carefully to make the right judgment. The scriber marks the diamond blank with Indian ink to indicate that the diamond is to be divided along this line. When drawing lines, draw lines in the direction of the diamond grain as far as possible.


V. The Cutting of Diamond
The cutting methods for diamonds include splitting and sawing.
(1) Splitting: the splitting worker will delimit the diamond line on the set fixed, and then use another diamond along the cutting line to cut a notch, and then put the square edge cutter on the notch, with a hammer on the cleaver with the appropriate force percussion, the diamond will be split into two or more pieces along the texture direction.
(2) Sawing: most diamonds are not suitable for splitting, then need to use sawing processing. Because of the high hardness of diamond, only diamond can cut diamond, so the saw blade is a round plate coated with diamond powder and lubricant on the edge. The diamond powder produced by Henan Crownkyn Company for diamond cutting has the characteristics of uniform particle size distribution, high hardness and strong wear resistance. The diamond is fixed on the clamp and the saw plate rotates at high speed to cut the diamond.
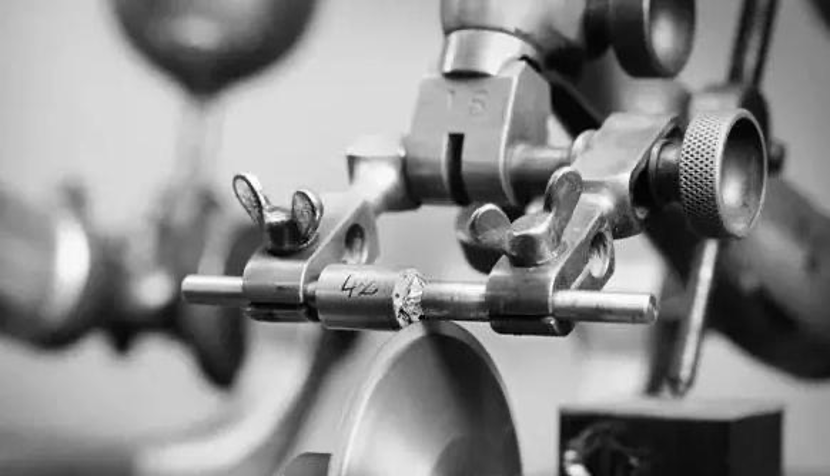

The introduction of modern laser technology into diamond cutting has greatly improved the machining efficiency of drill blanks. Now, Laser cutting technology is also the most common way of diamond cutting. Laser cutting will generate a lot of heat, need to keep water cooling. The advantage of laser cutting is that the cutting surface is very flat, and the consumption is very small.
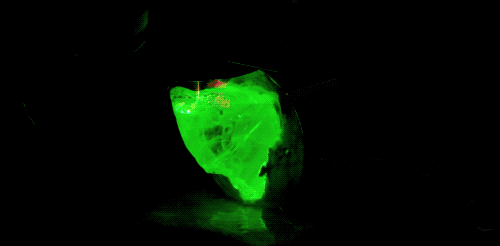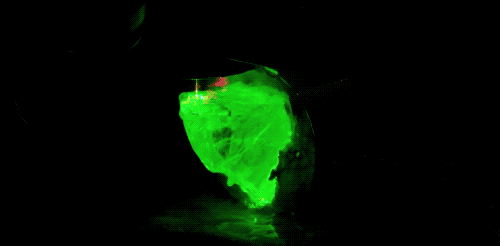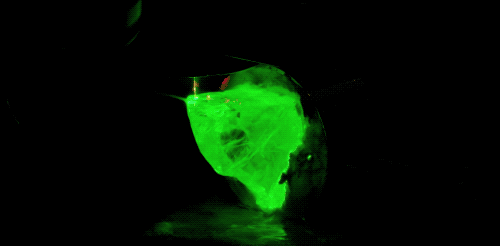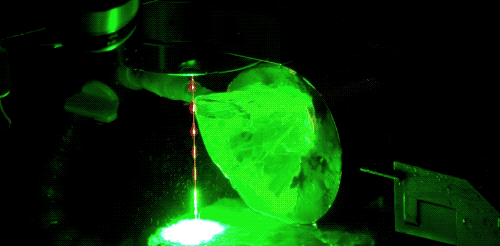
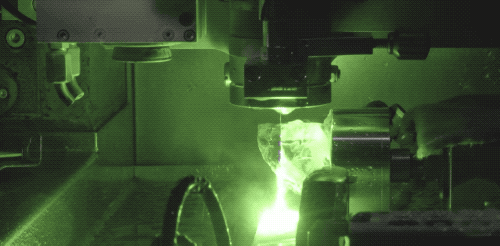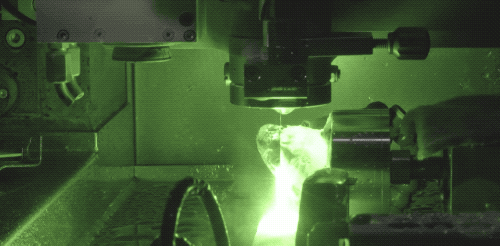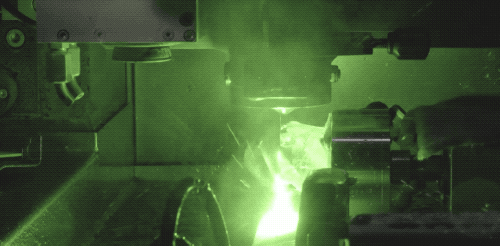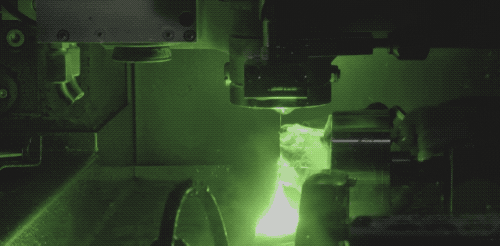
During laser processing, the high temperature generated by the laser changes the structure of diamond carbon into graphite, making the diamond surface black after cutting, and the black surface can be polished off by diamond powder.

IV. The shaping of a diamond by grinding
The sawed or split diamonds are sent to be rounded and shaped, and the diamonds are made into round, heart, oval, tip, emerald and other common cut flower shapes or other special shapes according to the design requirements. Since diamonds are by far the hardest natural substance known to man, only diamonds can polish diamonds. The diamond powder produced by Henan Crownkyn Company for diamond grinding has the characteristics of regular crystal shape, concentrated particle size distribution, extremely low impurity content, good thermal stability and high wear resistance.

Diamond polishing should rely on experience to grasp the basic shape of diamond, there are tripartite, octahedron, dodecahedron and crystal characteristics. The general method is to fix the diamond blank on the high-speed rotating lathe, and then use the diamond on the other arm to round the rotating rough diamond. When grinding, pick up the diamond every time to check the cut surface, and repeatedly check the degree of the cut surface.

With the development of technology, diamond design and cutting has been largely done by more accurate computers, but the last step of the polishing process can only be carried out manually and cannot be replaced by machines. A factory with nearly 100 employees can only finish more than 200 small diamond products in a busy day. If the diamonds are larger, the efficiency will be reduced to half.
The specific polishing process involves grinding all the facets on a cast-iron disc coated with diamond powder and lubricating oil to give the diamond an attractive glow. The process of grinding is usually to first make 8 large surfaces in the bottom layer and then make 16 facets. Add tip bottom, a total of 25 facets, and from this extension triangle facet, kite and waist facet, a total of 33 facets, so that a round diamond has 58 facets, if there is no tip facet, a total of 57 facets.
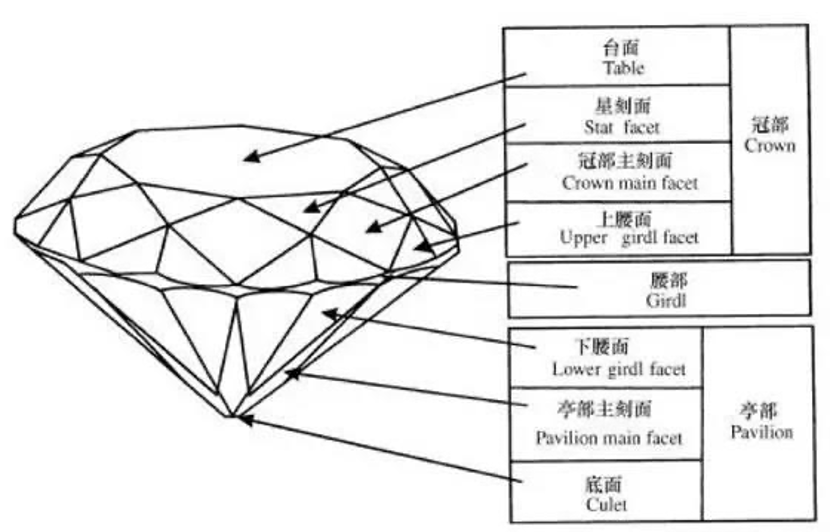
Not every diamond blank must go through all the above procedures, it must be based on the characteristics of the rough diamond itself and the goal to achieve. But any rough diamond, there are two processes are essential, is “marking” and “polishing flap”.
The position and angle of the surface produced by a carefully cut diamond are precisely calculated to give the diamond its maximum brilliance. The Angle at which a diamond is cut has a direct effect on the refraction and reflection of light.

Ⅶ. The Presentation of Diamonds
The lab-grown diamonds from crystal seeds to bright diamonds, not only need advanced equipment, more need to have rich experience, high degree of responsibility and concentration of the cutting division, in order to release all the brilliance of the diamond.

A diamond in a jewelry counter may have passed through many countries, through processing, setting, production before becoming a piece of diamond jewelry. With the progress of science and technology, the introduction of laser technology and electronic computer technology can make the design, cutting and grinding of the lab-grown diamond more accurate.
(World’s Largest Square Emerald Diamond Cutting)

-870x423.jpg)

